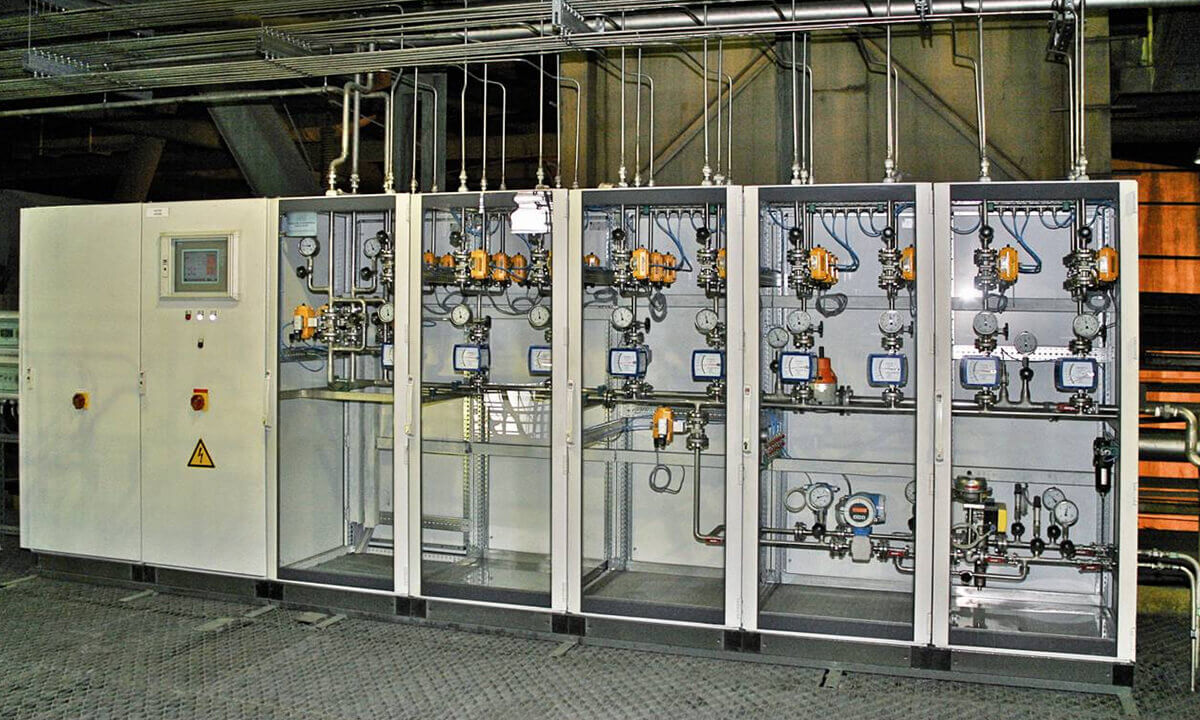
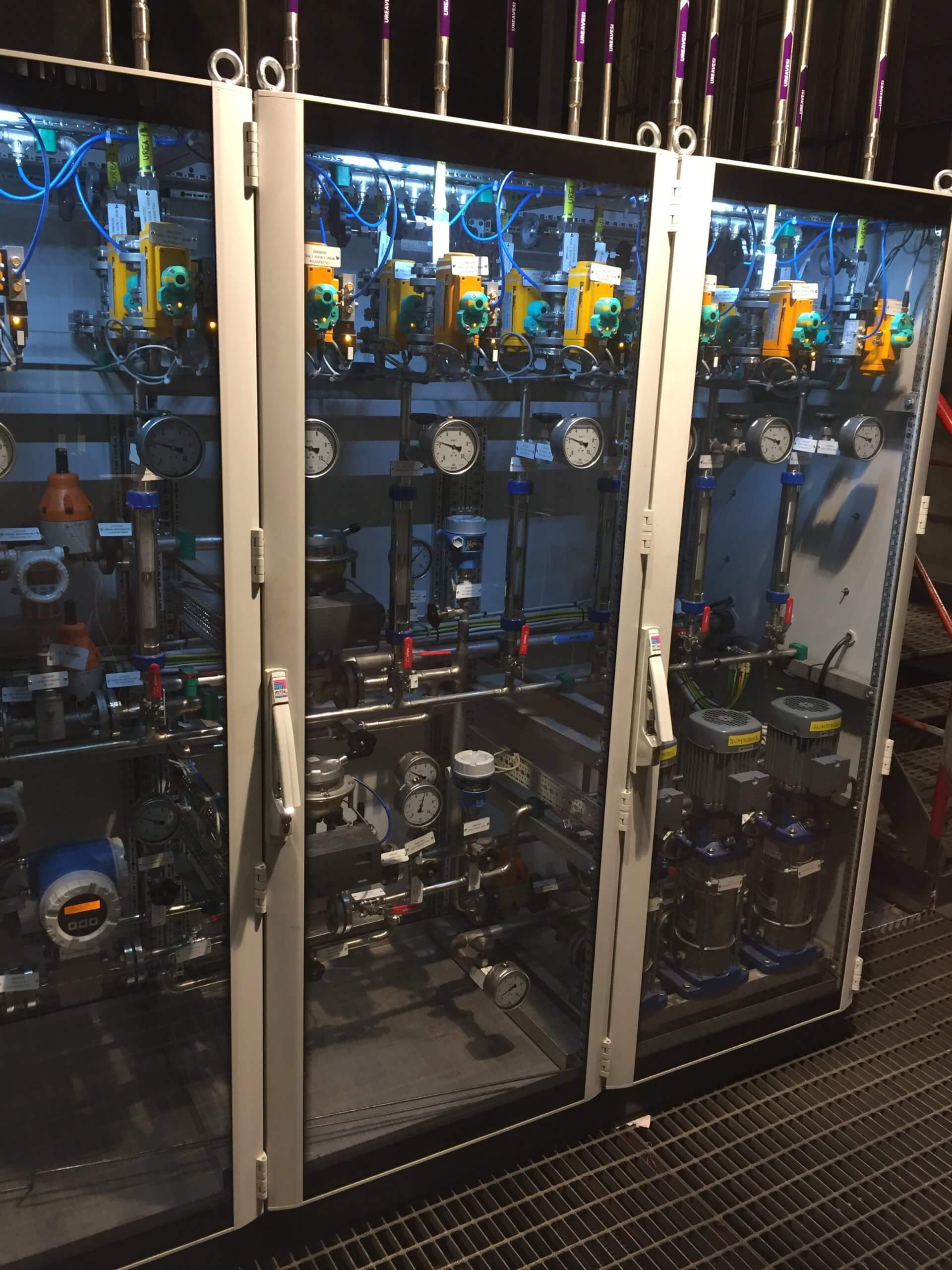
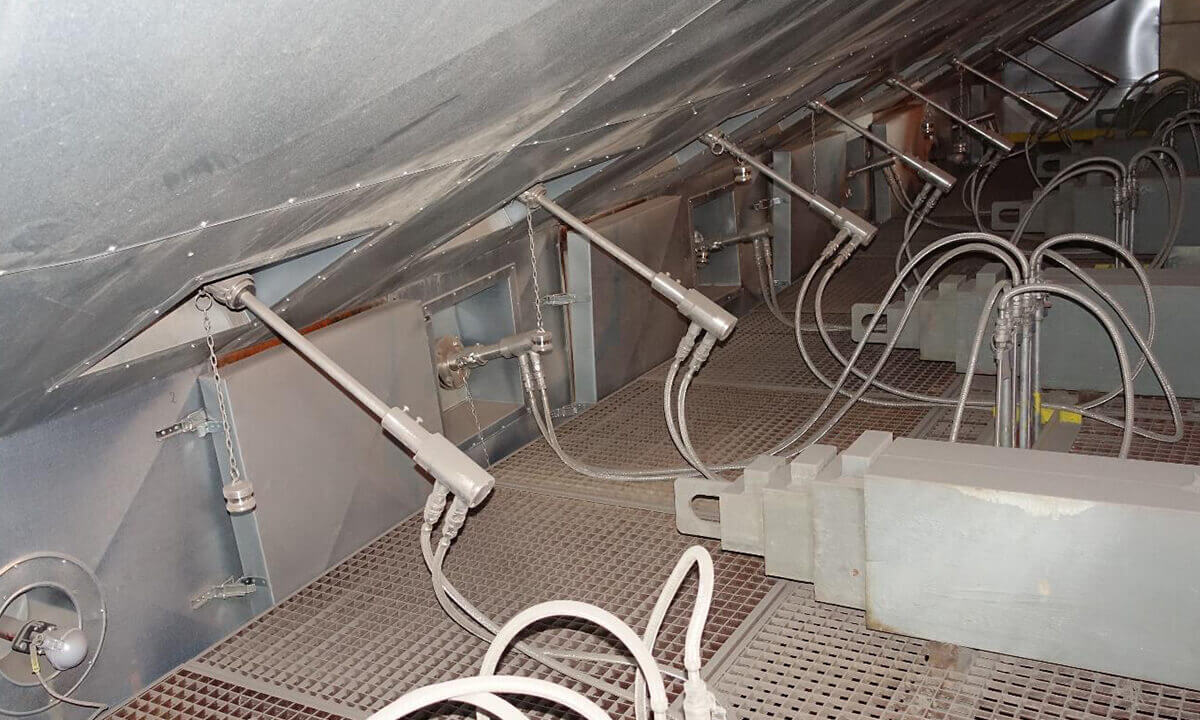
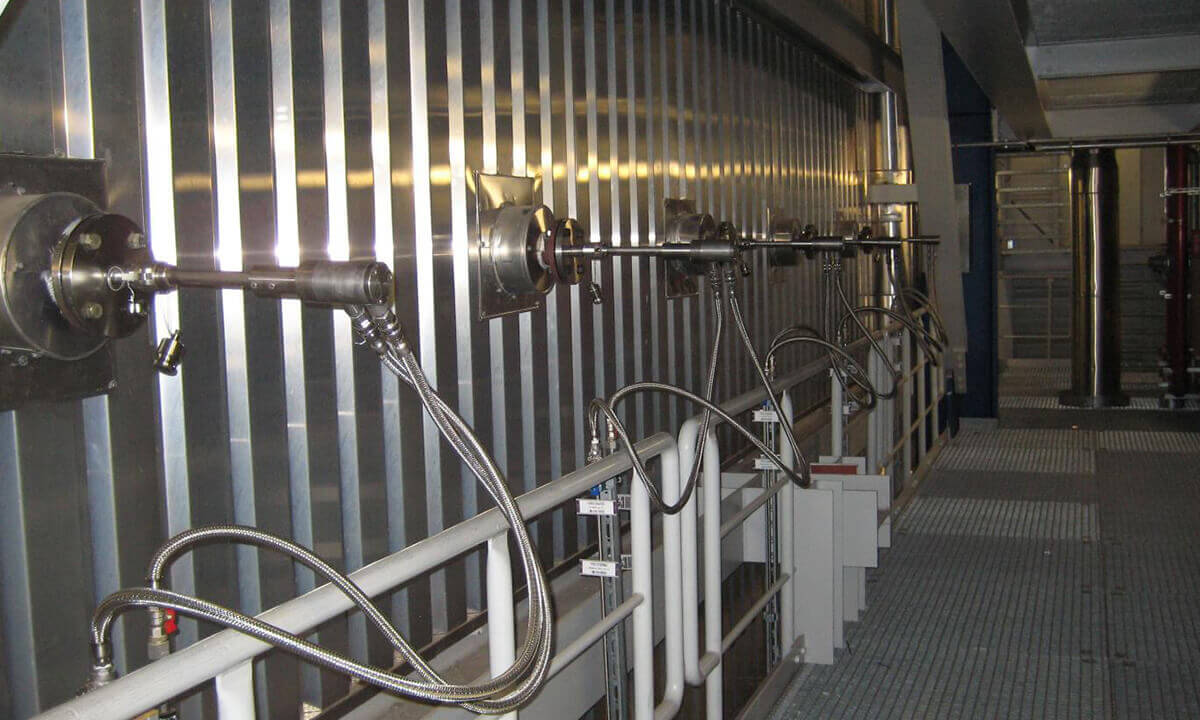
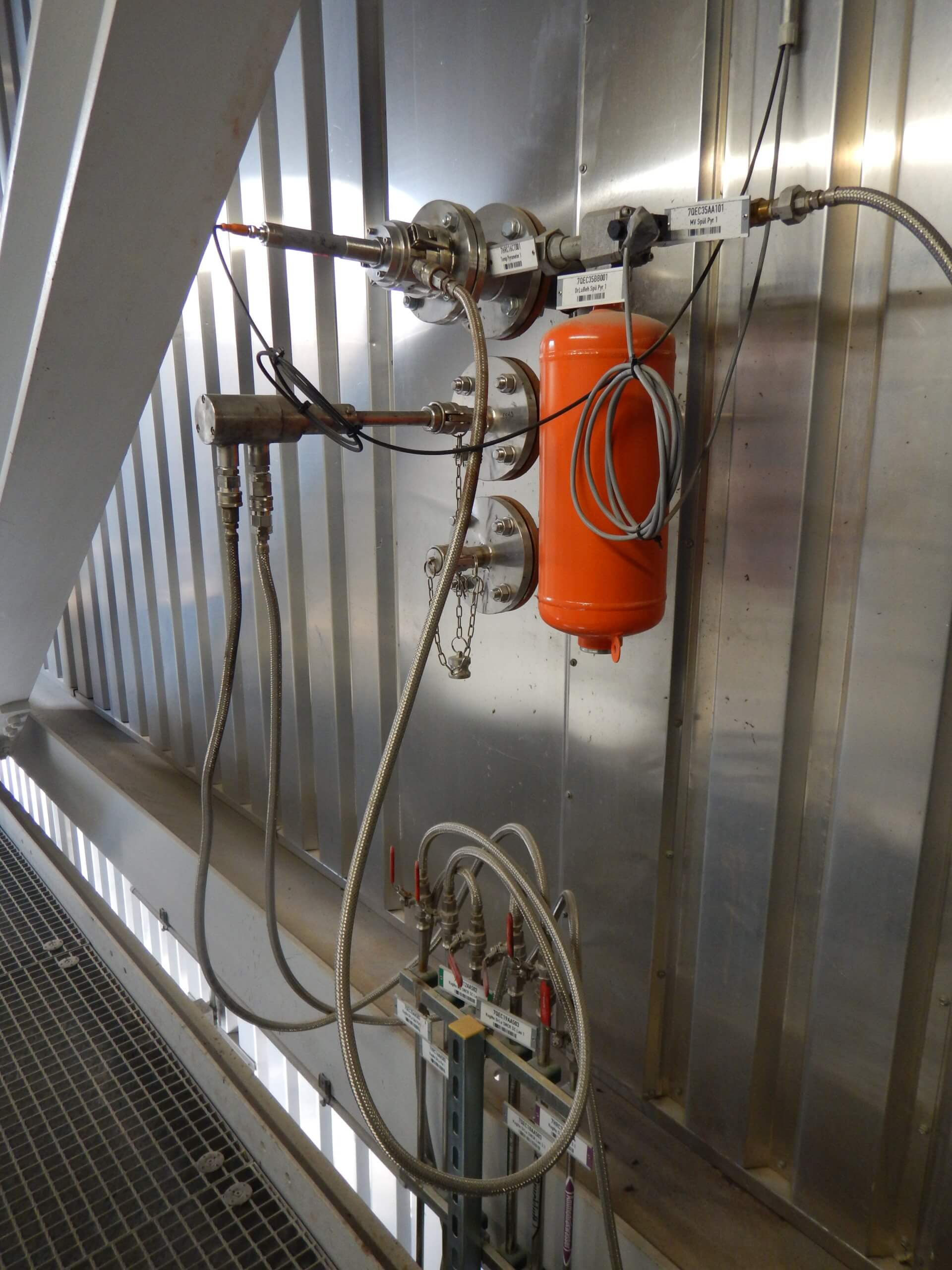
The SNCR Process | Single Lance Switching
FLUE GAS DENITRIFICATION (DeNOx)
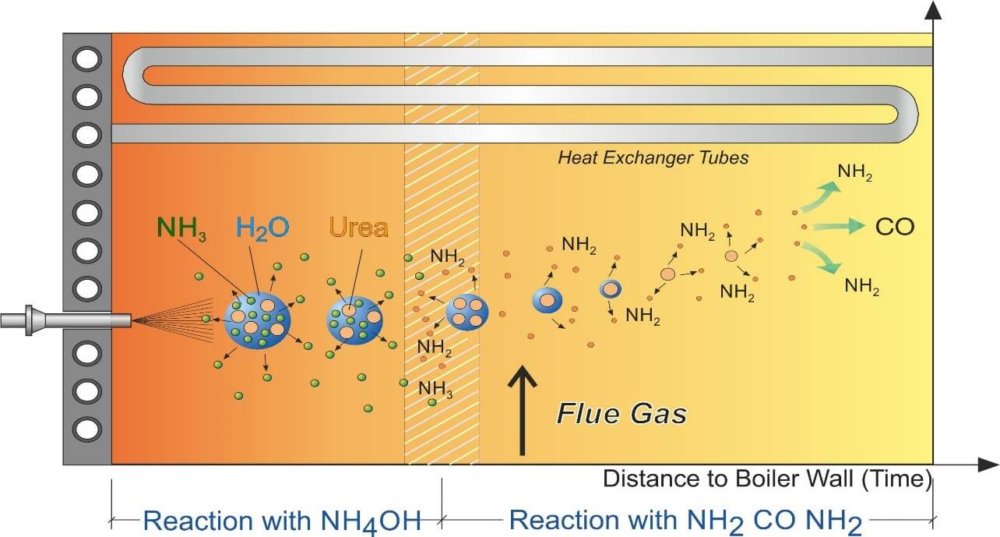
The so-called selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) is a process for reducing nitrogen oxides (NOx). For this purpose, a reducing agent is used that reacts with the environmentally harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) to form environmentally harmless nitrogen (N2) and water. The reaction temperature is between 850 and 1050 °C. SNCR systems are usually operated with an aqueous urea solution or ammonia water as a reducing agent.
The SNCR Process | Single Lance Switching
FLUE GAS DENITRIFICATION (DeNOx)
The so-called selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) is a process for reducing nitrogen oxides (NOx). For this purpose, a reducing agent is used that reacts with the environmentally harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) to form environmentally harmless nitrogen (N2) and water. The reaction temperature is between 850 and 1050 °C. SNCR systems are usually operated with an aqueous urea solution or ammonia water as a reducing agent.
ADVANTAGES OF THE SNCR PROCESS
The advantage of the SNCR process is the low level of economical and technical effort compared to an SCR process, which is operated after the boiler with the help of a catalytic converter and very often additional primary energy.
ADVANTAGES OF THE SNCR PROCESS
The advantage of the SNCR process is the low level of economical and technical effort compared to an SCR process, which is operated after the boiler with the help of a catalytic converter and very often additional primary energy.
-
Low investment costs, since the combustion chamber or the exhaust duct does not have to be converted
-
The SNCR process can be retrofitted in almost all existing boilers at short notice, as only the injection nozzles have to be installed for injection into the furnace
-
No re-heating of the flue gas necessary
-
No energy losses due to pressure losses
-
Suitable for a wide variety of fuels
-
Sufficiently high degrees of denitrification without a catalyst
-
The reducing agents are produced in large quantities and are available worldwide
-
No disposal of used catalyst elements necessary
-
Low investment costs, since the combustion chamber or the exhaust duct does not have to be converted
-
The SNCR process can be retrofitted in almost all existing boilers at short notice, as only the injection nozzles have to be installed for injection into the furnace
-
No re-heating of the flue gas necessary
-
No energy losses due to pressure losses
-
Suitable for a wide variety of fuels
-
Sufficiently high degrees of denitrification without a catalyst
-
The reducing agents are produced in large quantities and are available worldwide
-
No disposal of used catalyst elements necessary


EFFECTIVE IN NOX REDUCTION
The advantage of this process is the low complexity of the plant compared to an SCR process, which is operated after the boiler with the aid of a catalytic converter and very often additional primary energy. The SNCR system is installed in the first boiler pass above the furnace and is therefore part of the boiler. The essential fulfillment criterion for the operation of an SNCR process is the supply of the reagent ammonia or urea at the required flue gas temperature (between 850 and 1050 ° C) and the cross section of the first boiler pass. Since the flue gas temperature is very much dependent on the combustion control / regulation, there is also a direct connection to the performance and efficiency of the NOx reduction via the SNCR.

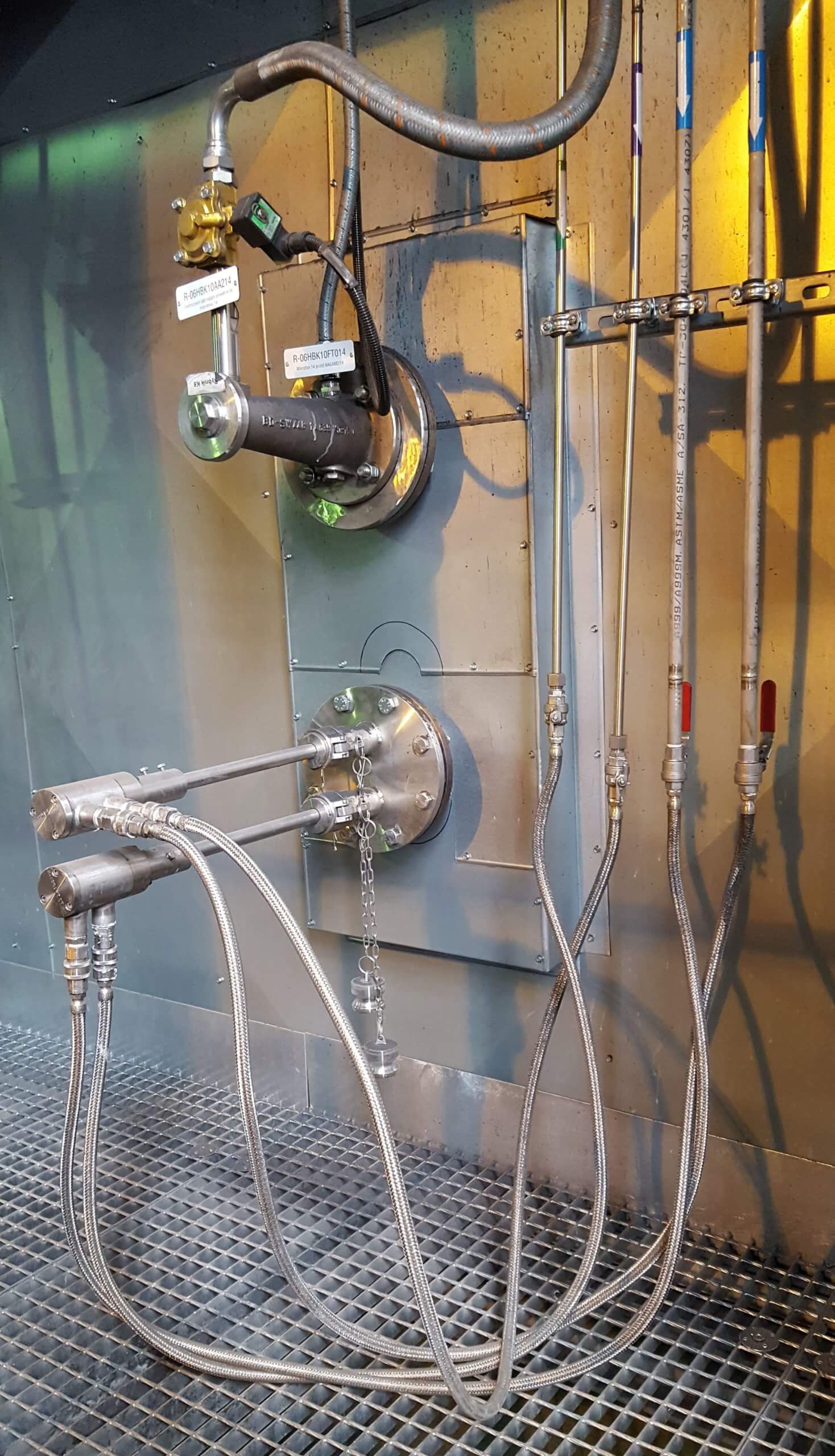
FLEXIBLE & MODULAR
The SNCR systems developed by Mehldau & Steinfath Umwelttechnik can be easily retrofitted into existing incineration systems thanks to their flexibility and modular design and in many cases exceed the legal requirements. The investment costs of our supplied SNCR systems are determined by the operator's requirements. They only amount to around 10 to 20 percent of the costs for catalytic processes and are generally economically far superior.
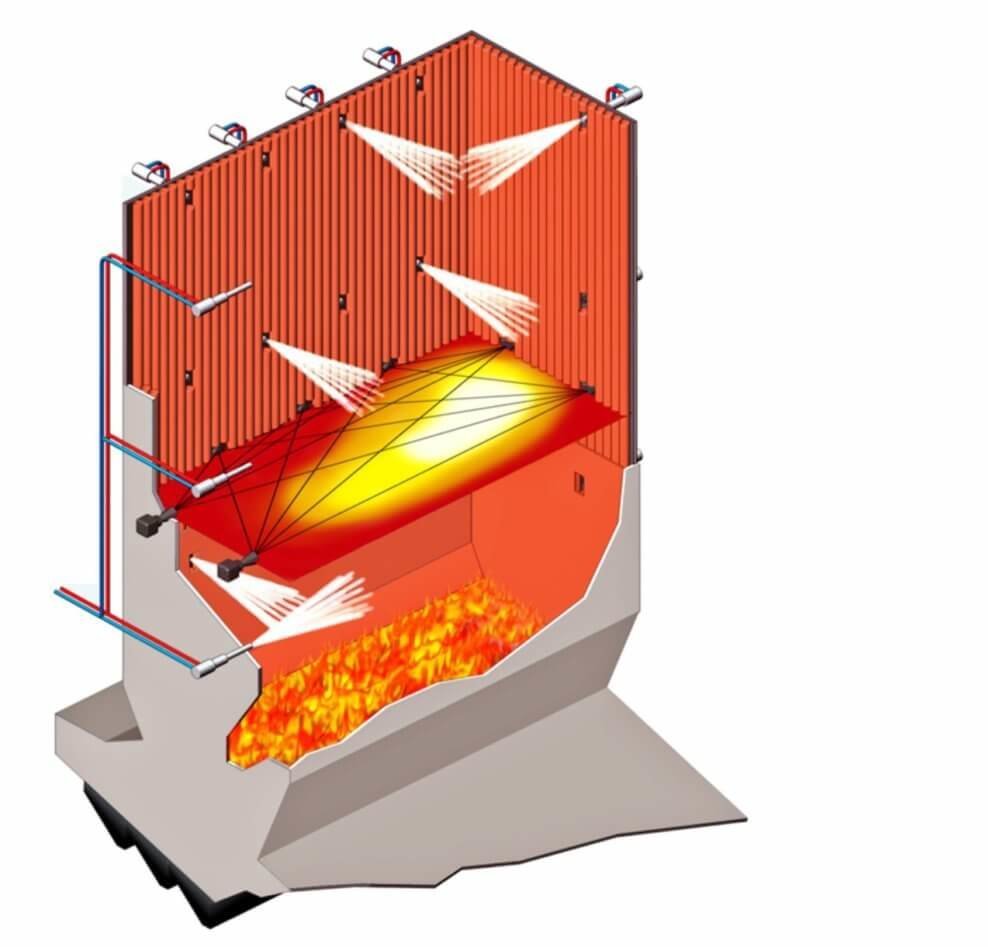

SINGLE LANCE SWITCHING
In order to ensure that the reducing agent is always injected into the optimum range of the temperature window, which is most effective in terms of NOX separation, NH3 slip and reducing agent consumption, in modern systems, the individual injection lances, and thus not the entire level, switched depending on the flue gas temperatures at the respective injection points.
The advantages of individual lance switching are:
-
Greater efficiency
-
Low NOx emissions
-
Low NH3 slip
-
Low CO emissions
-
Low consumption of reducing agents
Interested?
Find out more about the topic on individual lance switching in our paper.
TWIN-NOx
New generation of SNCR technology
Our patented TWIN-NOx® process combines the advantages of the reducing agents ammonia water and urea and thus achieves the best results.
With the TWIN-NOx® process, the different reaction behaviors of urea solution and ammonia water are specifically applied. Both reducing agents are used alternately or as a mixture, depending on the operating conditions. The respective advantages can thus be used alternatively or in combination, depending on requirements, in order to expand or shift the effective temperature range for the NOx separation and thus to significantly improve the performance of the SNCR process.
Interested?
Find out more about the topic on TWIN-NOx in our paper.

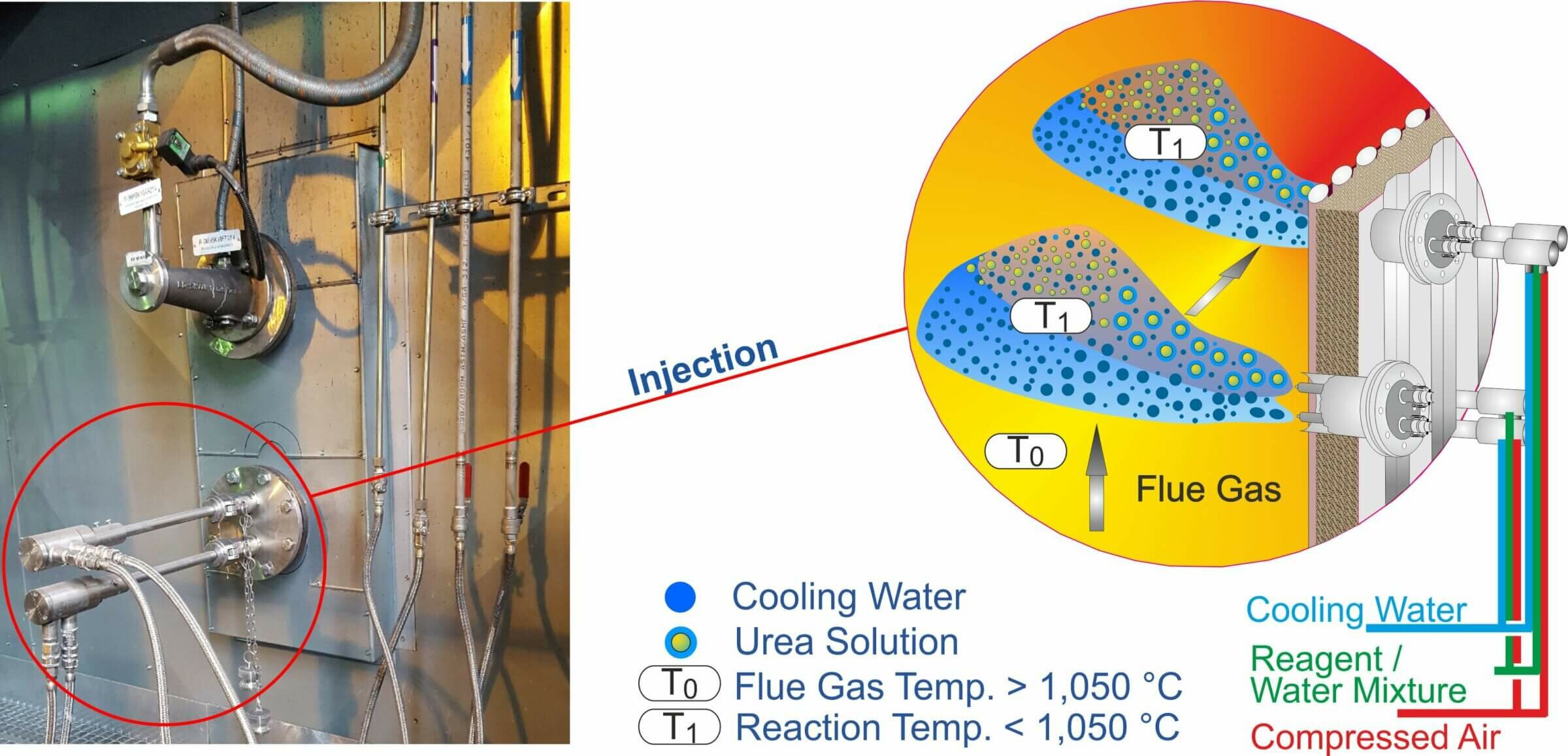
SELECTIVE COOLING
Selective cooling is a patented process with which the flue gases are locally and temporarily cooled down to the effective temperature at those points where the flue gas temperatures are too hot. Temperature imbalances can be compensated for with the injection of cooling water (selective cooling) so that each injection lance can be operated in the optimal temperature range in order to increase efficiency and minimize NH3 slip. To ensure that only those zones that are too hot are "selectively" cooled in the event of temperature imbalances, only a single or a group of cooling lances is specifically activated depending on the temperature profile, which significantly reduces cooling water consumption and thus heat loss in the boiler and Slip is kept low. By switching the cooling with water on or off, a second or third injection level for reducing agent can be omitted in many cases.
Interested?
Find out more about the topic on Selective Cooling in our paper.

Downloads
ALL ABOUT SNCR
- Mehldau & Steinfath Umwelttechnik GmbH
- 2019.09 Waste Management 9 IRRC Vienna Complying With The New EU NOx Emission Standards
- 2017.09 PG Asia Bangkok Future Oriented SNCR Technologies Selective Cooling+
- 2016.09 Waste Management 6 IRRC Vienna Efficient Monitoring, Mass NOx Profile
- 2017.06 PG Europe Cologne Appl Of SNCR Tech In Coal Fired Boilers
- 2016.09 PG Asia Seoul Advanced Features Of SNCR Technologies
- 2016.07 PG Africa Johannesburg Complying With New NOx Emission Standards
- 2015.10 Waste Management 5 IRRC Vienna New Developments Of An Effective SNCR Control System
- 2016.01 Energie Aus Abfall 13, Berlin Überwachung, Regelung, NOx Massenstrom
- 2015.06 PG Europe Amsterdam SNCR Tailor Made SNCR To Meet Future Emission Standards For Power Boilers
- 2014.06 PG Europe Cologne Next Generation Of SNCR Technologies
- 2013.06 PG Europe Vienna SNCR Process For Coal Fired Boilers Experiences And Potential For The Future
- 2013.05 VGB Flue Gas Cleaning Rotterdam Replacement Of An SCR By An SNCR Wijster+
- 2011.12 PG International Las Vegas Advanced SNCR Technology+
- 2010.06 PG Europe Amsterdam Advanced SNCR Technology For Coal Fired Boilers 200 MWel In Germany And 225 MWel In Poland
- 2008.06 PG Europe Milano SNCR BAT For NOx Reduction In Waste To Energy Plants+